Declarative Device Management (DDM)
Declarative Device Management (DDM)
Section titled “Declarative Device Management (DDM)”What is Declarative Device Management (DDM)?
This is what apple says about DDM:
Declarative device management is an update to the existing protocol for device management that can be used in combination with the existing MDM protocol capabilities. It allows the device to asynchronously apply settings and report status back to the MDM solution without constant polling. This is ideal for performance and scalability.
Declarative device management gives organizations more confidence that devices are in the desired state and that essential data is kept secure, even without internet connectivity. And from a user perspective, it provides a much more responsive experience.
Status reporting allows a device to share information about its current state, and if there are any changes, these can be reported to the server proactively without having to poll the device for updates. Extensibility is built into the protocol to ensure that declarative management is designed for the present and the future.
Prerequisites
Before implementing Declarative Device Management (DDM), it is crucial to ensure that the devices being managed have the required hardware and software capabilities. Compatibility with the operating system, firmware, and management tools is essential for a successful implementation.
DDM necessitates devices running at least iOS/iPadOS 15 and macOS 13. These operating systems introduce the necessary features and frameworks to enable autonomous decision-making based on predefined rules and configurations. Therefore, it is important to verify that the devices in your organization meet these requirements before adopting DDM.
Software Updates
Declarative Device Management (DDM) facilitates the automated scheduling of software updates, ensuring that devices remain current with the latest patches and enhancements. By defining update policies and schedules, you can ensure timely and efficient software updates across your managed device fleet.
With DDM, you can set rules within the declarative data model that dictate how software updates should be managed on devices. These rules can include criteria such as update availability and scheduling preferences. Devices autonomously check for available updates based on these predefined rules and apply them accordingly.
How does it Work
DDM employs three key principles to enhance the software update process, surpassing traditional MDM setups:
- Firstly, for configurations, your MDM instructs the device on how to handle updates. The device then executes these guidelines while also notifying and empowering the user to initiate updates at their convenience.
- Secondly, predicates serve as the foundation for logical operations that dictate the sequence of software updates. This includes managing both seed builds and critical security patches that become available on the device.
- Lastly, real-time status reporting ensures that administrators are promptly informed of any issues, allowing for immediate action.
Setup the Intune Policy
Go to Intune Portal – Devices – MacOS – Configuration Profiles – Create – New Policy – Platform MacOS – Profile type Settings Catalog – Create
Name your policy e.g MacOS – Declarative Device Management and give a description if you want.
Click Add settings and browse to Declarative Device Management

Click on Software update and click select all these settings.
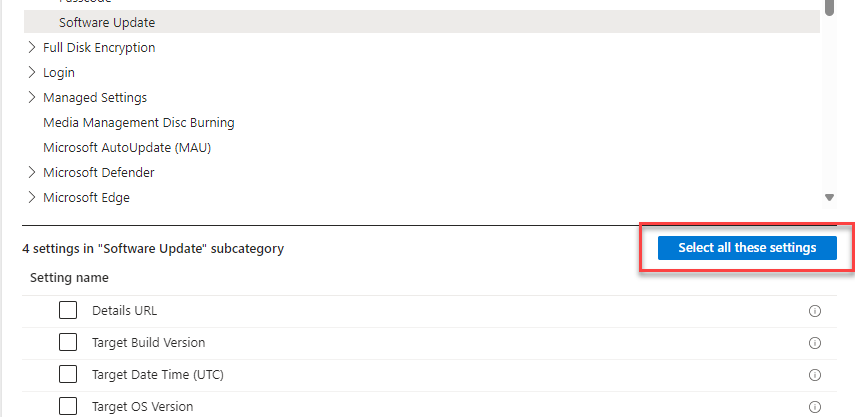
Configure the settings:
- Details URL: Enter a web page URL that has more information on the update. This site has all the info regarding the MacOS versions: https://developer.apple.com/documentation/macos-release-notes
- Target Build Version: Enter the target build version to update the device to, like 20A242.
- Target Local Date Time: Enter the local date time value that specifies when to force the installation of the software update. This setting uses the yyyy-mm-ddThh:mm:sss format.
- Target OS Version: Enter the target OS version to update the device to. Here you can get the version numbers: https://support.apple.com/en-us/109033
These settings will update your MacOS device to the latest Sonoma update by 07/06/2024
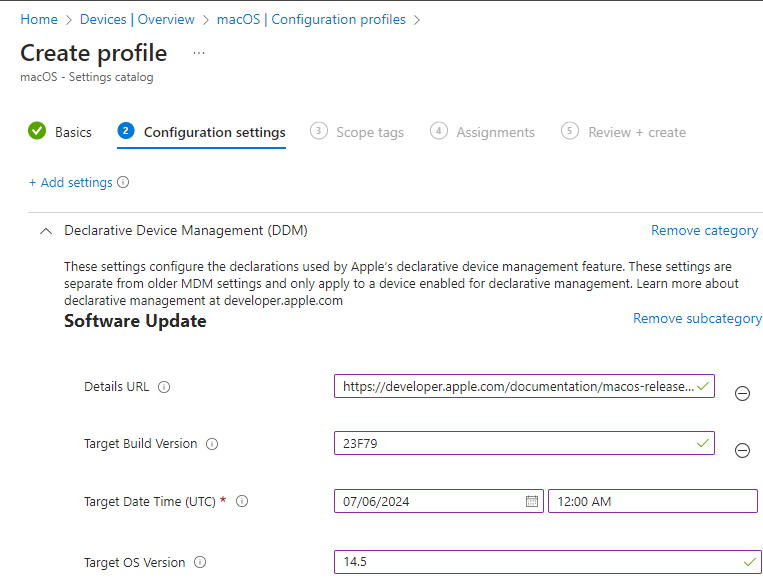
Click next, fill in scope tags if you have them, assign the policy to your desired group and click create
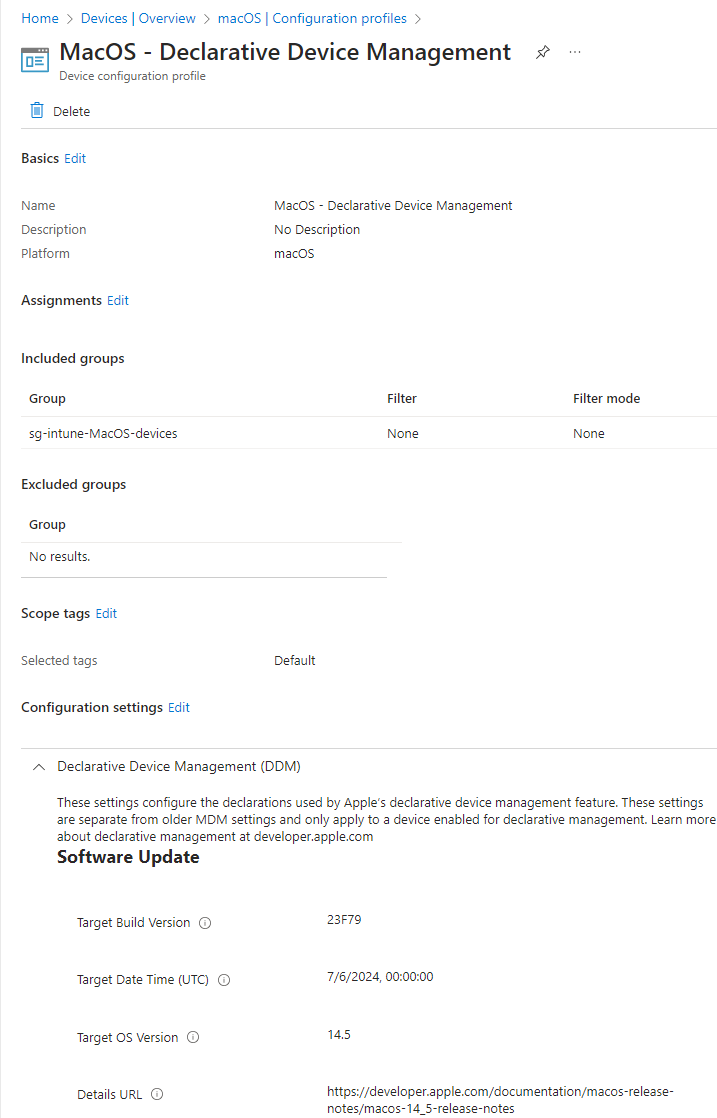
Your policy will look like this:
As the policy arrives on your device you will get a pop-up like this:
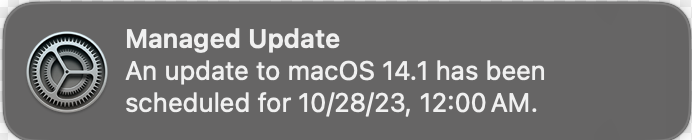
This is not a notification from my machines as they are already on 14.5, this is a screenshot i took from the internet

Delay visibility of updates
When configuring managed software updates, you might want to hide updates from users for a specific time period. To do this, use a settings catalog policy that sets an update restriction.
A restriction period allows you to test an update before it becomes available to users. Once the restriction period ends, users will be able to see the update. If your update policies haven’t already installed it, users can then choose to install the update themselves.
To create a restrictions policy, navigate to the Settings catalog > Restrictions. Some settings you can use to defer an update include:
- Enforced Software Update Delay
- Enforced Software Update Major OS Deferred Install Delay (macOS)
- Enforced Software Update Minor OS Deferred Install Delay (macOS)
- Enforced Software Update Non OS Deferred Install Delay (macOS)
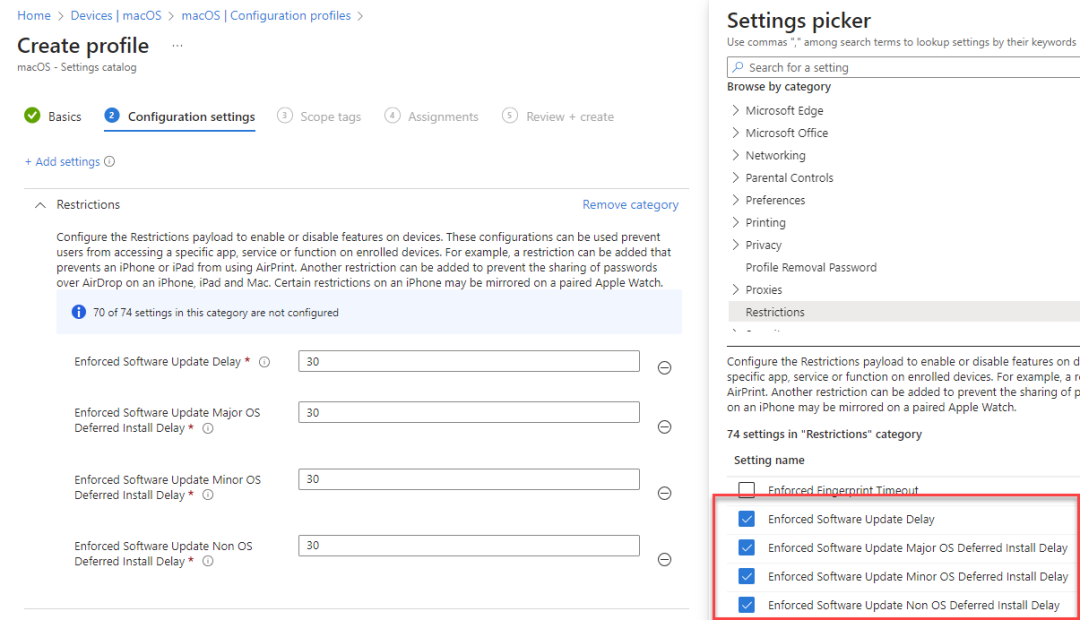
Settings explained:
Section titled “Settings explained:”Enforced Software Update Delay: Sets how many days to delay a software update on the device. With this restriction in place, the user doesn’t see a software update until the specified number of days after the software update release date. This value is used by Force Delayed App Software Updates and Force Delayed Software Updates. Requires a supervised device in iOS. Available in iOS 11.3 and later, and macOS 10.13.4 and later.
Enforced Software Update Major OS Deferred Install Delay: This restriction allows the admin to set how many days to delay a major software update on the device. When this restriction is in place the user sees a software update only after the specified delay after the release of the software update. This value controls the delay for Force Delayed Major Software Updates. Available in macOS 11.3 and later.
Enforced Software Update Minor OS Deferred Install Delay: This restriction allows the admin to set how many days to delay a minor OS software update on the device. When this restriction is in place the user see a software update only after the specified delay after the release of the software update. This value controls the delay for Force Delayed Software Updates. Available in macOS 11.3 and later.
Enforced Software Update Non OS Deferred Install Delay: This restriction allows the admin to set how many days to delay an app software update on the device. When this restriction is in place the user sees a non-OS software update only after the specified delay after the release of the software. This value controls the delay for Force Delayed App Software Updates. Available in macOS 11.3 and later.
With these settings in place you can configure multiple policies to create different update rings.
Wrap Up
Section titled “Wrap Up”Wrap Up Declarative Device Management (DDM) is a groundbreaking approach that enables mobile devices to operate autonomously and proactively. By allowing devices to make decisions based on predefined rules, DDM enhances performance, scalability, and security.
With DDM, organizations can enjoy several advantages. Improved performance and scalability are achieved as devices function independently and efficiently, minimizing the need for constant supervision. This results in faster response times in large-scale deployments and frees up valuable resources for other strategic initiatives.
Enhanced security and compliance are also significant benefits of DDM. By enforcing predefined rules and configurations, organizations can ensure that devices adhere to established guidelines. Policies related to password complexity, encryption requirements, app installation permissions, network access controls, and more are automatically enforced by the devices themselves.
In conclusion, Declarative Device Management revolutionizes mobile device management practices by empowering devices to operate autonomously based on predefined rules.
Moving on……