Basic Tenant Setup
Overview
Section titled “Overview”After meeting the Prerequisites we turn over to the setup of the tenant and equipment of policies & apps.
- Create groups & filters
- Create compliance policy
- Create configuration policies
- Evaluate updating
- Deploy apps
- Create scripts (optional)
- Create custom attributes (optional)
Introduction
Section titled “Introduction”All management tasks can be done within Intune > Devices > macOS - here you can configure and monitor everything:
1. Groups & filters
Section titled “1. Groups & filters”First, let’s create a group/filter where your Macs are automatically added to target policies and other contents.
Entra dynamic group query
(device.deviceOSType -eq "macMDM")Intune filter query
(device.model -contains "Mac")2. Compliance policy
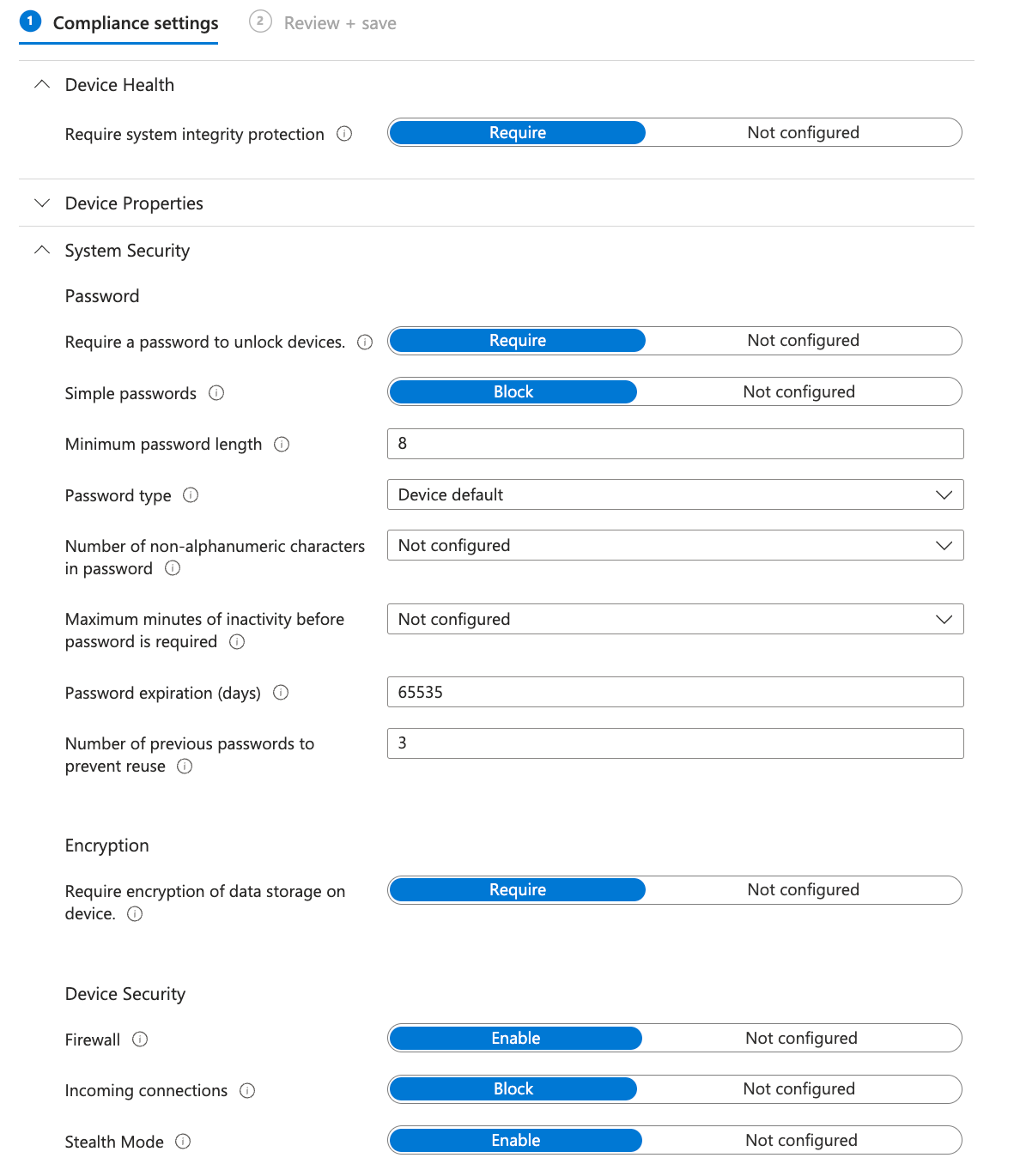
Section titled “2. Compliance policy”A compliance policy is the fundamental part of the Intune management, because it determines if the Mac is fullfilling basic requirements in order to access corporate resources. Let’s start with a basic version of it:
3. Create configuraiton policies
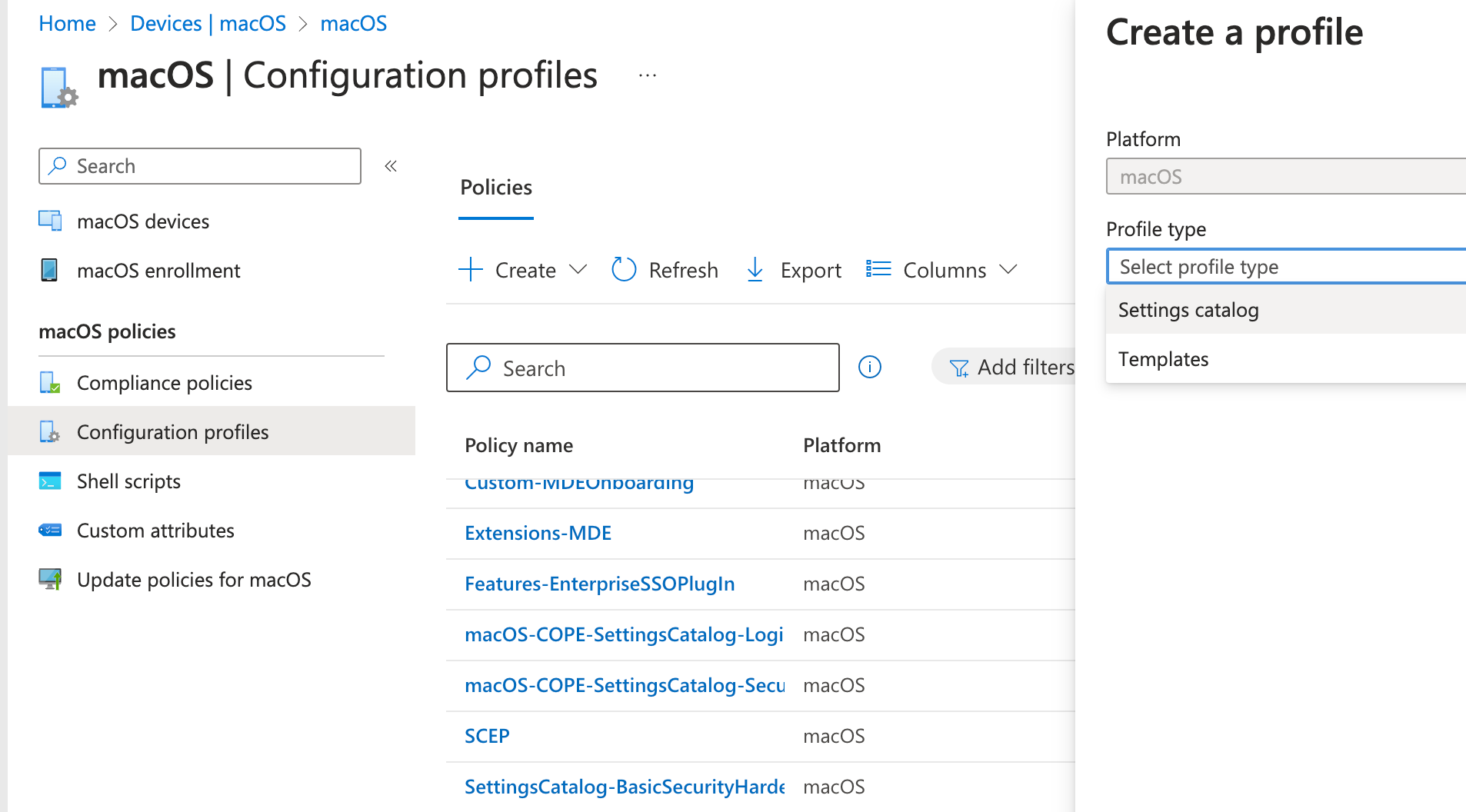
Section titled “3. Create configuraiton policies”Configuration is a wide area and offers a lot of options. You can configure nearly every aspect of the system to get your desired look & feel. Some recommended policies are found here
4. Evaluate updating
Section titled “4. Evaluate updating”When it comes to OS updating, you have to main built-in options:
- macOS updates policy in Intune (less control options)
- Settings Catalog DDM update configuration (recommended)
5. Deploy apps
Section titled “5. Deploy apps”Intune supports app deployment to:
- Deploy apps from different repositories/stores
- Configure apps and monitor the status
- Provide apps as available from Company Portal
There are different sources with different behaviors to get apps from:
- Built-in in Intune: Microsoft 365 Apps, Edge, Defender for Endpoint
- Web clip or link (just a shortcut to a URL)
- Apple Volume Purchase Program (VPP), requires Apple Business Manager - apps are ‘aquired’ there and synced to Intune
- macOS types:
- DMG = Disk Image, basically just an application file
- PKG = Package, more configuration options (insatller behavior)
6. Create scripts (optional)
Section titled “6. Create scripts (optional)”macOS scripts are based on shell and can be deployed to managed endpoints. Here you can find a repo with some inspiration.
7. Create custom attributes (optional)
Section titled “7. Create custom attributes (optional)”Custom attributes are shell scripts that read out a system value in a string, integer or date. This is practical for custom inventory data or retrieving a status on the system.